To approach the topic of art and blockchain, we need to define what a so-called NFT is.
NFT (Non-fungible Token):
An NFT (Non-fungible Token) is a unique, digital,
cryptographic token on a blockchain.
It enables the verification, tracking change of status
of digital and non-digital goods and services.
The 3 most common applications of NFT in art can be divided into 3 categories:
- Proof of ownership for offline-art
- Digital art connected (minted on the blockchain) with a NFT
- Generative art on the blockchain
1. Proof of ownership for offline-art
The easiest concept to understand is probably the application as proof of ownership of offline-art.
For example, a NFT token is generated that proves the ownership of the painting “The Japanese Bridge” by Claude Monet.
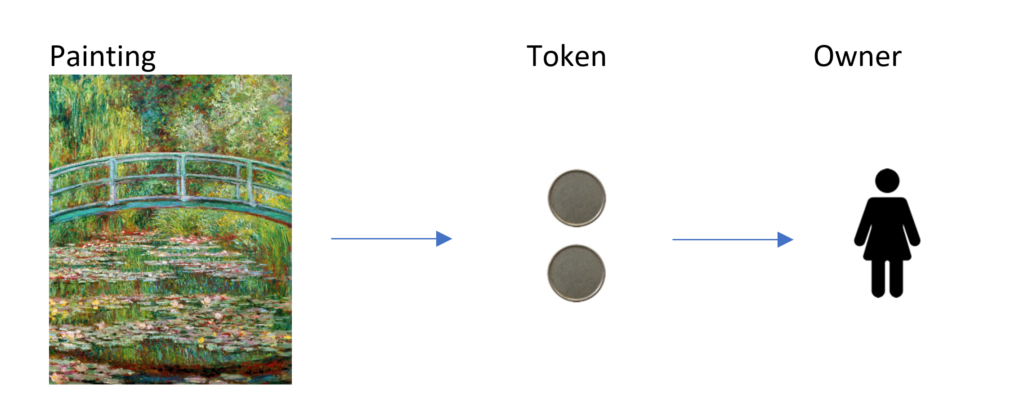
The owner now has the possibility to sell one of the tokens to someone else. As a result, another person acquires partial ownership of this work of art.
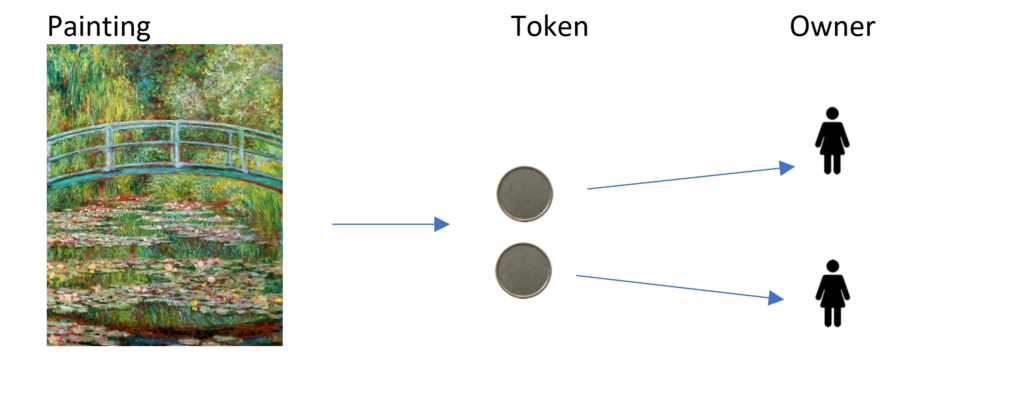
The artwork remains untouched in situ (museum/collection), partial ownership transfer was settled within minutes by a simple entry in the blockchain, quick, worldwide, secure, without lawyers nor papers and without physical contact.
In our example we now have two owners that both hold a partial ownership of the painting.
NFTs can also serve as proof of authenticity for offline-art, but it would go beyond the scope of this article to describe this application.
2. Digital art connected (minted on the blockchain) with a NFT
Now we are moving into the purely digital world.
Art on the blockchain is
a young, emerging niche
An artist creates a digital artwork. This is connected to a token on the blockchain in a process called minting. In the case of digital art, not only does proof of ownership arise immediately, but also verifiable proof of authenticity.
After this process, the artist can sell the digital artwork. When the artwork is sold, the price and the new owner are automatically recorded on the blockchain. Change of status, ownership, sale price, automatic royalty distribution and authenticity of an artwork can be tracked on Etherscan ( https://etherscan.io/ ), among others.
Etherscan makes it easy to read all transactions that take place on the Ethereum blockchain. However, the numbers and designations are often not very meaningful to the untrained eye. With a little practice, however, simple correlations can be recognised and transactions verified. For experts, all transactions that have ever taken place on the blockchain can be traced and thus every work of art can be verified back to the artist.
The artworks themselves are usually stored on the IPFS (InterPlanetary FileSystem) and can be viewed on various trading platforms, at home on the digital picture frame, on any digital device or in a virtual gallery. The topic of virtual galleries will be presented in one of the next blog articles.
For beginners, I recommend the trading platform https://makersplace.com/ , where you can also trade in USD. A very nice and exciting marketplace to see the whole range of art. Also highly recommended is https://superrare.co/ . This platform trades exclusively in cryptocurrency.
This picture can be found here as a file and here on Etherscan

This artwork can be found here as a file and here on Etherscan

3. Generative art on the blockchain
The third category is, so to speak, the supreme discipline of digital art. This category is further divided into subcategories depending on how and to what extent the artwork is generated and stored on the blockchain, basic explanations of the main category follow.
technology has the potential to change the art world and everything beyond
Generative art is a work of art that only comes into being when a defined input takes place.
There is an algorithm and as soon as it is triggered, the artwork is created. The trigger can be a mouse click, an external event, for example a certain price of a cryptocurrency, or snowfall in Africa. There are unlimited possibilities for the artist.
As soon as the predefined event occurs, the algorithm is executed and the artwork is created.
In most cases, the variables that make up the definition and appearance of the artwork are extracted from the blockchain. This results in artworks that are unique.
Since these variables were extracted from the blockchain and the algorithm is a computer code, it is possible to store the entire artwork directly on the blockchain. It thus becomes unchangeable and is system agnostic.
Examples for art like this are the projects:






Summary
Art on the blockchain is a young, emerging niche in art. Sales are still small compared to the traditional art market, but some works have already exceeded the USD 1 million mark. The underlying technology has the potential to change the art world and everything beyond.
For further information and inspiration on how NFTs can be useful for you, please do not hesitate to contact me.
Patrick Neuenschwander ( p.neuenschwander@gmail.com )